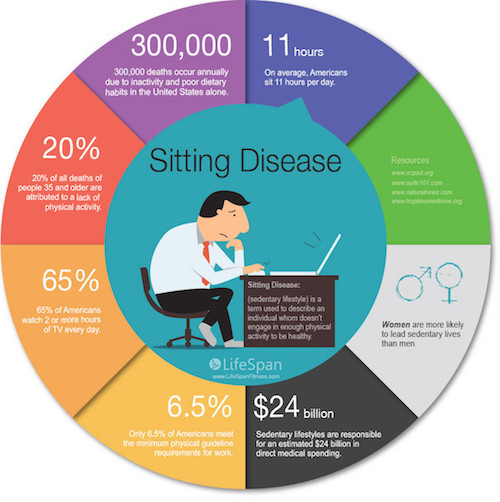
If you’ve been having some back or neck pain while working lately, it might be time to assess things. The dangers of sitting badly are real.
What’s your office setup like?
That’s one of the first of many questions I ask my patients.
And just like my patients, chances are there’s a few practical things you can do to improve your workstation setup.
Firstly, if you’re interested in investing a little into your office, I suggest you look at my colleague’s article about ergonomic products and also home office essentials guide.
So here you go, my process for creating an ergonomic workstation.
Why Use An Ergonomic Workstation?
You might ask the question, why are some offices are paying a lot of money to have ergonomic workstations installed for their employees?
It’s simple.
Ergonomic workstations set up a conducive working posture throughout the day, which makes employees healthier and happier.
Poor work environments have the potential to cause poor efficiency, morale, and health for employees.
Computer related injuries
A huge concern for employers is that they’re injuring their workers.
Office-related injuries due to a combination of lengthy sitting and poor posture include:
- lower back pain
- neck and shoulder pain,
- decreased blood circulation throughout the body
- repetitive use injuries to the wrists and hands.
Staring at a computer screen all day can cause blurred vision, fatigue, and headaches.
Long term issues
Employees may think that these injuries are temporary, but researchers say otherwise, claiming injuries over time can turn into chronic conditions.
These conditions include nerve impingements, blood pressure changes, metabolic changes, and joint subluxation.
Desk Setup: How To Sit At A Desk
-
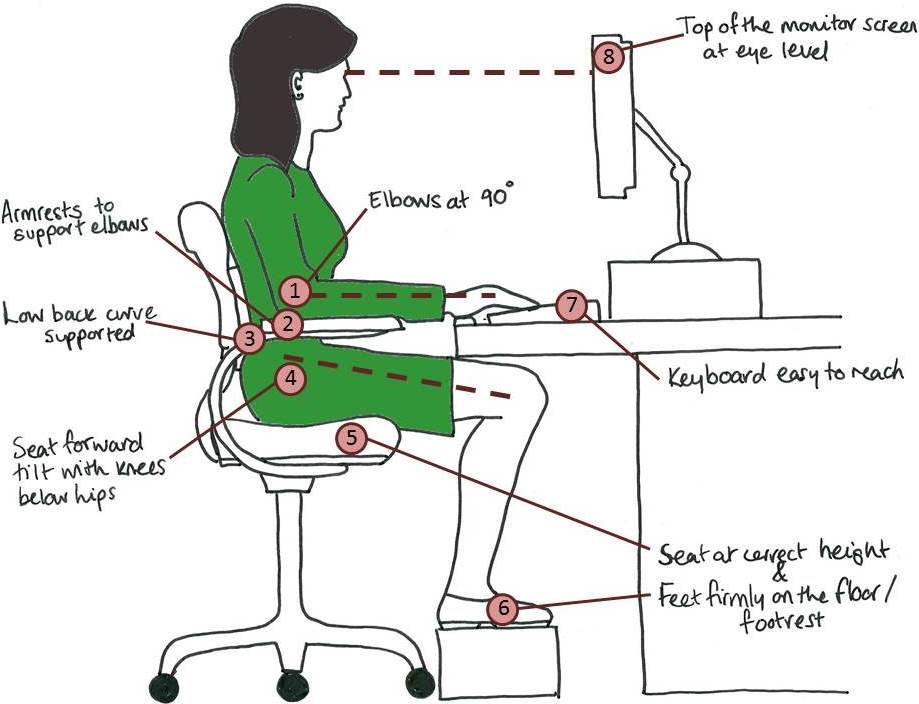
Lorna Rose Osteopathy
We’ve all experienced back pain while sitting. But believe it or not, there is a more natural way to sit at a desk for several hours.
In order to determine how you can sit safely at your workstation, you need to break down your entire body’s resting position:
Posture

The typical desk posture that every office worker is familiar with includes the shoulders and neck hunched forward.
Obviously, this occurs due to fatigue and/or due to the computer’s placement along with its accessories (i.e. keyboard, mouse, etc.).
How to improve your posture
Start with making the conscious effort to maintain an upright position with your shoulders back and your neck upright (your chin should be making a 90 degree angle with your neck).
Once you have gotten that position down, you will start to notice what items in your workstation need modifying.
Posture Correctors
There are a number of posture correctors the market which help train you to sit up straight. Some popular devices include the Upright Go and the Lumo Lift.
Desk height & positioning
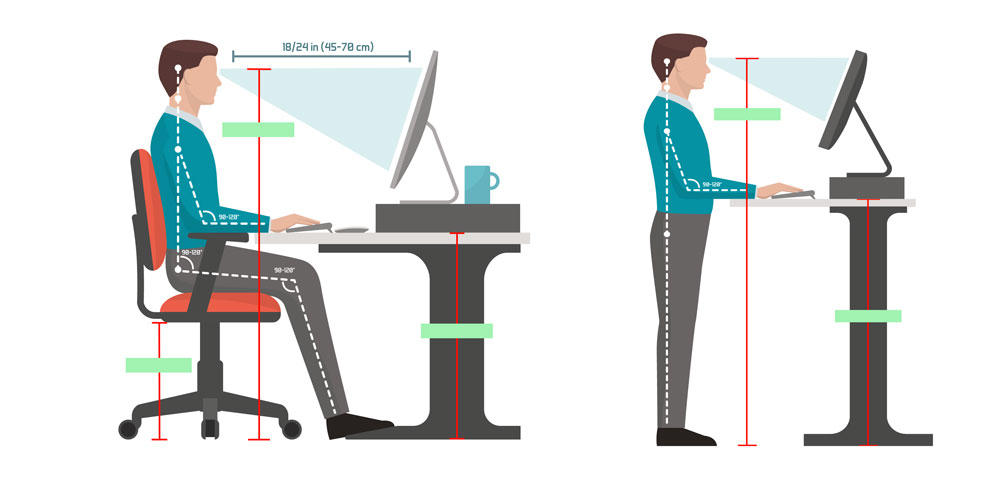 Make sure that the height of your desk matches your upright posture.
Make sure that the height of your desk matches your upright posture.
Your desk should be high enough so that you can pull your chair in without knocking your knees into the furniture.
The desk should be low enough so that your keyboard can be used with your elbows angled at 90 degrees or slightly greater.
You should also be able to pull your computer screen forward enough on the desk space so that you don’t have to lean in and strain to see your work.
Proper keyboard & mouse position
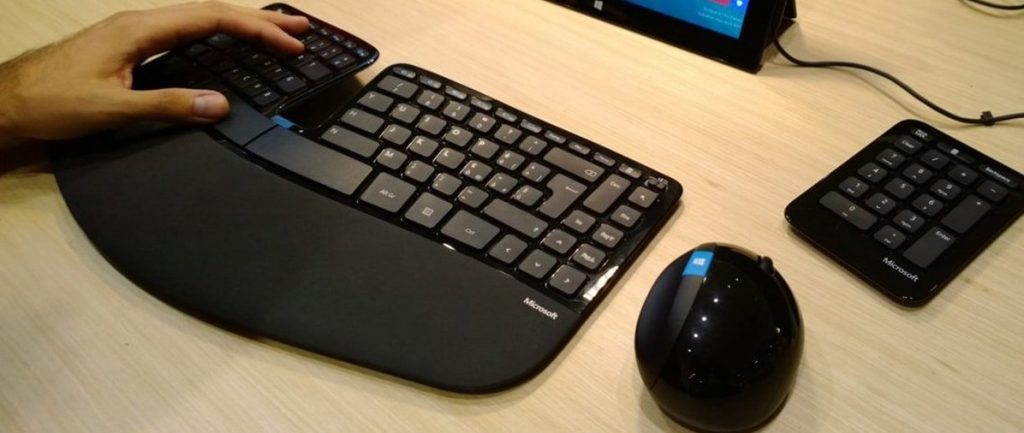

The keyboard and the mouse should be placed in such a way so that your elbows are extended past 90 degrees.
Your wrists and fingers should be neutral or drop lower than neutral.
Prolonged hyperextension and closure of the elbows can lead to nerve impingements, decreased circulation to the hand muscles, and repetitive use injury to the joints.
Computer positioning
The computer screen needs to be placed close enough to you so that you are not straining your eyes and neck forward to see your work.
Furthermore, the height of the screen should allow you to keep an upright posture.
Ergonomics for laptops
Do not work with your laptop in your lap. Prop it up on your desk at a reasonable height. You can use a laptop riser to achieve that.
Consider connecting a different keyboard to your laptop so that you can adjust the space between the keys and the computer screen.
If you’re working in bed (Not that I recommend it!) make sure you use an ergonomic bed tray.
Ergonomic Chairs
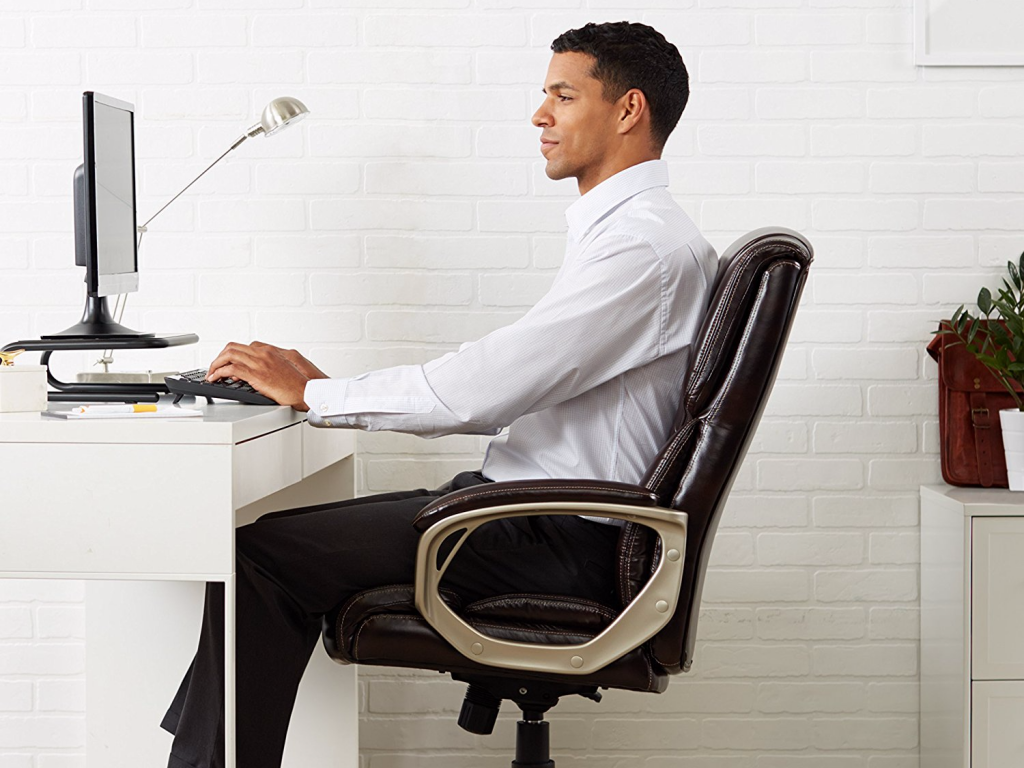

We always recommend to our clients and readers to invest in a comfortable ergonomic chair.
If you have an ergonomic chair, make sure you’re sitting right..
This includes adjusting the height so that your feet are flat on the floor. Scoot your hips all the way back into the chair so that your spine has the entire back support available.
Lower or raise the arm rests so that your shoulders are relaxed and that your elbows are angles to at least 90 degrees at rest. If you must, add a pillow or cushion to provide yourself with extra lower back support.
Some standard office chairs are just not going to cut it, in which case investing in an ergonomic chair is appropriate. Here are some useful considerations to look for in an ergonomic chair.
Seat height adjustment
As discussed previously, height adjustment is key in an ergonomic chair. You want to be able to adjust your height accordingly in order to best match the desk and computer set-up.
Back tilt tension
This is a little knob feature that you can use to adjust how easily it is for you to rock back in your chair.
It’s really up to you, but you want enough tension for the full back support while you still have the option to recline back a few degrees whenever you need to reposition and stretch your spine.
Lumbar support
This refers to the contour of the back support that outlines your lower back.
An ergonomic chair will probably have a portion of the back support that curves slightly inward to fit the natural S-curve of your spine and to minimize lower back pain.
If your seat is lacking in this support, you might consider buying a lumbar support pillow.
Arm support adjustment
As mentioned earlier, you want an ergonomic chair that has height-adjustable arm supports since arm size is not universal. The height should be set in a position where your shoulders are relaxed at rest.
Back height adjustment
Alongside the arm-rests, an ergonomic chair should include a back height adjustment option so that you can line up the contour back support to your own spine.
Ergonomic Room Setup
Aside from applying ergonomics for your posture, consider what other room modifications need to be made to enhance your productivity at work:
Lighting
Some office workers are prone to headaches or migraines, which can be triggered by the typical fluorescent lighting in an office space.
Others may feel like they don’t have enough light to complete their work, and need a suitable desk lamp.
Figure out what your preferences are in order to minimize your eye and head strain. Bring in shaded glasses or a desk lamp if needed.
Airflow
Do you like having the extra fan or do you freeze out when the giant air conditioner comes on during the summertime? Ask your employers about cooling options if you heat up easily, or remember to bring in those extra clothing layers.
Noise
Can you tune out office-related background noise while working? Or do those clacking shoes and and mouse clicks in your surroundings drive you crazy?
Ask your employer about whether or not you can bring in headsets or earmuffs to deter the noise so that you can work better. You could also consider a white noise machine.
Smell
Do the minor musky scents of the office distract your work? See if your employer will allow you to spruce up your workspace with pleasing scents so that you can get back to work.
Tips For Staying Healthy
Note that sitting at an ergonomic workstation setup for 8 hours straight will not solve all of your physical problems. Your body is not designed for sitting that long, so it is important that you take the opportunity to move throughout the day:
- Change your position or work activity at least once every hour
- Create a workout regimen in which your exercising for 30 minutes at least 3 times a week outside of your work schedule
- Stretch and stand up every few minutes
- Perform muscle building exercises like squats, lunges, pushups, jumping jacks, and shoulder shrugs
- Go on a short walk in the office
Taking regular breaks
Get up and get away from your desk for the sake of movement as well as for the sake of your eyes and mind. You have been staring at a computer screen for a long time so allow your eyes and brain to adjust.
Office Stretching Exercises
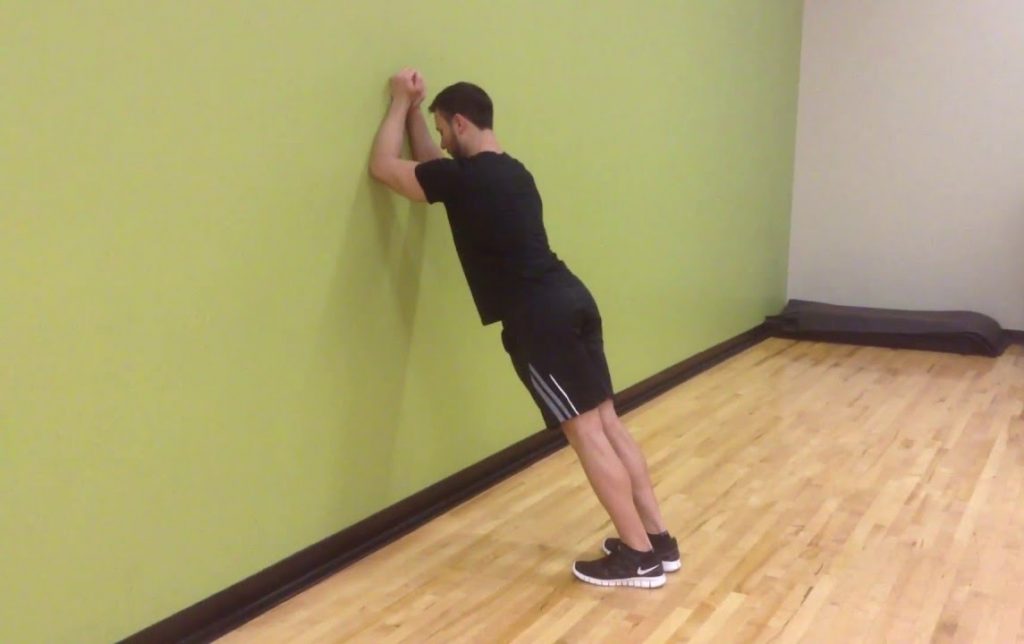

Good stretching exercises can help counteract the effects of bad posture. Do these posture exercises at the end of a long day:
- Sit against a wall: Also called the right-angled wall stretch, you lie on the floor with your bum against the wall, legs straight up against the wall.
- Stand against a wall: Take off your shoes and stand up straight with the heels touching the wall. Keep your chin down and lift your arms up and down, like fluttering wings, but slowly, while staring straight ahead of you.
- Simply lie on the floor on your back: This position is also practiced in yoga as it has many benefits for the body. You lie down on the floor, with the feet spread and the toes facing outward. Your arms should be by your side, palms up, chin down.
Ergonomic Accessories To Consider

Ergonomic chair
We’ve talked in great lengths about the benefits of an ergonomic chair.
If your standard office chair isn’t doing the trick, this would be a worthy investment for your health and your work demeanor.
If you need some advice about ergonomic chairs, feel free to have a read through these resources:
- Ergonomic chairs: check out our reclining chairs and executive chairs guide to get you started.
- Kneeling chairs: an alternative way to sit at a desk, kneeling chairs are known to be quite effective for many people.
- Saddle chairs: common among healthcare professionals, some ergonomic saddle chairs have been effectively designed for the office.
- Ergonomic stools: used for sitting or standing, these ergonomic stools are a great way to engage your core while being stationery.
Monitor arms and laptop risers
There are desk arms that can be attached to the back of monitors so that you can swivel and adjust the screen to the height and angle of your choosing. Laptop risers allow you some more freedom as well.
Ergonomic mouse & keyboard
An ergonomic mouse and keyboard products that are shaped differently that standard equipment in order to better contour to your wrists and hands while working to minimize risk for injury.
Keyboard trays
Keyboard trays that have swing-away and height adjustment options are fantastic alternatives to just a normal desktop set up.
You have the ability to move the keyboard to a position tailored to your needs, opening up the angle of your elbows, and allowing for your wrists and fingers to drop down preventing risk for repetitive use injury.
Foot rests
Ergonomic foot rests can be installed to your chair or to your desk so that you can adjust the height of your feet as well as the angle of your knee joints while working for increased circulation.
Standing desk or converter
Some people are not built for sitting at work at all, but have the physical capacity to stand at work instead.
Your office work can be just as productive if you are standing on your feet for most of the day.
Standing desks allow you the opportunity to stand but can also come with converter options so that you can still sit when needed. You may also consider a standing desk stool, which encourages active sitting while perching.
The formula for the perfect ergonomic workstation setup will not be the exact same for everyone. Some workers may be able to work with the equipment they already have while others will have to go out and purchase new products.
In any case, office workers should put their health at the top of their priority lists and start by treating themselves well during business hours.
Children's Ergonomics
Although children are not confined to an office setting like adults, you still need to pay attention to how children work, play, and sit in a variety of settings.
In the past few years, children’s ergonomics has become an area of focus for ergonomists, especially in the classroom.
Manufacturers have also caught up with safety guidelines, producing quality ergonomic chairs & desks, art desks, and even toddler activity tables.
Sources
https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/adult-health/in-depth/office-ergonomics/art-20046169
https://myhealth.alberta.ca/Health/Pages/conditions.aspx?hwid=zm2298
https://www.worksafe.qld.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0006/83067/guide-ergo-comp-workstations.pdf
https://www.safety.uwa.edu.au/topics/physical/ergonomics/workstation
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/328338658_Ergonomic_Diagnosis_of_a_Computer_Workstation
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3985273/
https://worldwidescience.org/topicpages/w/workstation+design+ergonomics.html
https://ehs.princeton.edu/book/export/html/72





